Types of motion
I.Rectilinear or translatory:The motion in which a particle moves along a straight line, is called rectilinear motion.
Ex.Bullet fired from a gun,
Ball rolling off a table.
II.Circular or Rotatory:The motion in which a particle moves along a circular path,called circular or rotatory motion.
Ex.A car turning through a curve in a race track.
Artificial satellite orbiting the earth.
III.Oscillatory and Vibratory:The motion in which a body moves to and fro or back and forth repeatedly about a fixed point,is called oscillatory motion.if in oscillatory motion,the amplitude is very small,then the motion is called vibratory motion.
Ex.Sound wave,Pendulum,Swings.
One two and three Dimensional Motion:
One-Dimensional Motion:When the position of the object changes only in one direction,then the motion of an object is called one-dimensional motion or body moves along a line,then the motion is called one dimensional motion.
Ex.Motion of a car on the road,
Object falling freely under gravity
Two-Dimensional Motion:When the position of the object changes in two direction ,then the motion of an object is called two-dimensional motion.
Ex.The motion of a planet around the sun.
Three-Dimensional Motion:When the position of the object changes in three direction,then the motion of an object is called three-dimensional motion.
Ex.Flying bird,
When body moves in a space.
Terms related with Motion
Reference point:A fixed point or a fixed object with respect to which the given body changes its position is known as reference point.
Position:it is the point in space where an object is present with respect to the reference point.
Distance:The actual length of the path covered by a moving body irrespective of the direction in which the body travels.
Path Length:It is the length of curve joining the initial and final positions along which the particle has actually moved.
Speed:The time rate of change of position of the object in any direction is called speed of the object
Speed(v)=Distance travelled(s)/Time taken(t).
SI unit is m/s.
Speed is always positive and can never be negative and zero.
Types of speed
(i)Uniform speed:If an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time,then its speed is called uniform speed.
(ii)Non-uniform speed:If an object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time,then its speed is called non-uniform speed.
(iii)Average speed:The ratio of the total distance travelled by the object to the total time taken is called average speed of the object.
Average Speed=Total distance travelled/total time taken
If an object travels distances a,b,c,d.. with t1,t2,t3,t4..then
Average Speed=a+b+c+d../t1+t2+t3+t4.
(iv)Instantaneous Speed:The speed of a particle at any instant of time is known as its instantaneous speed.
Displacement:A straight line between initial position and the final position of the body along with direction is known as displacement.
SI unit metre.
Displacement of the object can be zero,negative or positive.
Velocity:The time rate of change of displacement of a body is called its velocity.it is vector quantity.
Velocity=Displacement/time
SI unit is m/s.
Velocity of an object can be changed by changing the object's speed or direction of motion or both.
The velocity of an object is taken to be positive if the object is moving towards the right of origin and is taken to be negative if the object is moving towards the left of the origin.
Types of velocity
Uniform velocity:If an object covers equal displacement in equal intervals of time,then it is said to be moving with a uniform velocity.
Non-uniform velocity:If an object covers unequal displacement in equal time intervals,then it is said to be moving with non-uniform velocity.
Average velocity:The ratio of the total displacement to the total time taken called average velocity.
Average velocity = total Displacement/total time taken
if velocity of the object changes at a uniform rate,then
Average velocity = Initial velocity+final velocity/2 = u+v/2
Instantaneous velocity:The velocity of a particle at any instant of time is known as its instantaneous velocity
SI unit is m/s.
Acceleration:The time rate of change of velocity of a body is called acceleration.it is a vector quantity denoted by a and its SI unit is m/s2
Acceleration = Change in velocity /Time interval
If in a given time interval t the velocity of a body changes from u to v then acceleration is expressed by
a=final velocity - initial velocity/t = v-u/t.
When the velocity of a body increases with time,acceleration is positive and when the velocity of a body decreases with time then acceleration becomes negative.
Types of Acceleration
Uniform acceleration:If the velocity changes uniformly at equal intervals of time,then acceleration is said to be uniform acceleration.
Ex.A body falling down from a height.
Non-uniform acceleration:If the velocity of the particle does not change equally in equal intervals of time,then the acceleration is said to be non-uniform acceleration.
Ex.The acceleration produced in spring-block system is non- uniform acceleration.
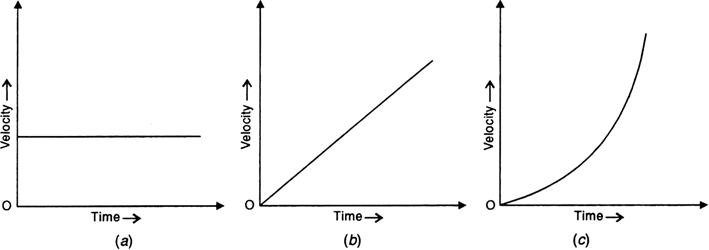
Velocity-Time graph
I.When an object is moving with constant velocity(0 acceleration)
Then the graph is a straight line parallel to time axis.same as displacement-time graph when object is at rest.
II.When an object is moving with positive constant acceleration having some initial velocity
Then the graph is straight line.
III.When an object is moving with constant positive acceleration having zero initial velocity
Then the graph is a straight line passing through the origin.fig(b)
IV.When an object is moving with increasing acceleration having zero initial velocity
Then the graph is a curve.fig(c)
I.Rectilinear or translatory:The motion in which a particle moves along a straight line, is called rectilinear motion.
Ex.Bullet fired from a gun,
Ball rolling off a table.
II.Circular or Rotatory:The motion in which a particle moves along a circular path,called circular or rotatory motion.
Ex.A car turning through a curve in a race track.
Artificial satellite orbiting the earth.
III.Oscillatory and Vibratory:The motion in which a body moves to and fro or back and forth repeatedly about a fixed point,is called oscillatory motion.if in oscillatory motion,the amplitude is very small,then the motion is called vibratory motion.
Ex.Sound wave,Pendulum,Swings.
One two and three Dimensional Motion:
One-Dimensional Motion:When the position of the object changes only in one direction,then the motion of an object is called one-dimensional motion or body moves along a line,then the motion is called one dimensional motion.
Ex.Motion of a car on the road,
Object falling freely under gravity
Two-Dimensional Motion:When the position of the object changes in two direction ,then the motion of an object is called two-dimensional motion.
Ex.The motion of a planet around the sun.
Three-Dimensional Motion:When the position of the object changes in three direction,then the motion of an object is called three-dimensional motion.
Ex.Flying bird,
When body moves in a space.
Terms related with Motion
Reference point:A fixed point or a fixed object with respect to which the given body changes its position is known as reference point.
Position:it is the point in space where an object is present with respect to the reference point.
Distance:The actual length of the path covered by a moving body irrespective of the direction in which the body travels.
Path Length:It is the length of curve joining the initial and final positions along which the particle has actually moved.
Speed:The time rate of change of position of the object in any direction is called speed of the object
Speed(v)=Distance travelled(s)/Time taken(t).
SI unit is m/s.
Speed is always positive and can never be negative and zero.
Types of speed
(i)Uniform speed:If an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time,then its speed is called uniform speed.
(ii)Non-uniform speed:If an object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time,then its speed is called non-uniform speed.
(iii)Average speed:The ratio of the total distance travelled by the object to the total time taken is called average speed of the object.
Average Speed=Total distance travelled/total time taken
If an object travels distances a,b,c,d.. with t1,t2,t3,t4..then
Average Speed=a+b+c+d../t1+t2+t3+t4.
(iv)Instantaneous Speed:The speed of a particle at any instant of time is known as its instantaneous speed.
Displacement:A straight line between initial position and the final position of the body along with direction is known as displacement.
SI unit metre.
Displacement of the object can be zero,negative or positive.
Velocity:The time rate of change of displacement of a body is called its velocity.it is vector quantity.
Velocity=Displacement/time
SI unit is m/s.
Velocity of an object can be changed by changing the object's speed or direction of motion or both.
The velocity of an object is taken to be positive if the object is moving towards the right of origin and is taken to be negative if the object is moving towards the left of the origin.
Types of velocity
Uniform velocity:If an object covers equal displacement in equal intervals of time,then it is said to be moving with a uniform velocity.
Non-uniform velocity:If an object covers unequal displacement in equal time intervals,then it is said to be moving with non-uniform velocity.
Average velocity:The ratio of the total displacement to the total time taken called average velocity.
Average velocity = total Displacement/total time taken
if velocity of the object changes at a uniform rate,then
Average velocity = Initial velocity+final velocity/2 = u+v/2
Instantaneous velocity:The velocity of a particle at any instant of time is known as its instantaneous velocity
SI unit is m/s.
Acceleration:The time rate of change of velocity of a body is called acceleration.it is a vector quantity denoted by a and its SI unit is m/s2
Acceleration = Change in velocity /Time interval
If in a given time interval t the velocity of a body changes from u to v then acceleration is expressed by
a=final velocity - initial velocity/t = v-u/t.
When the velocity of a body increases with time,acceleration is positive and when the velocity of a body decreases with time then acceleration becomes negative.
Types of Acceleration
Uniform acceleration:If the velocity changes uniformly at equal intervals of time,then acceleration is said to be uniform acceleration.
Ex.A body falling down from a height.
Non-uniform acceleration:If the velocity of the particle does not change equally in equal intervals of time,then the acceleration is said to be non-uniform acceleration.
Ex.The acceleration produced in spring-block system is non- uniform acceleration.
Average acceleration:The ratio of the total change in velocity of the object during motion to the total time.
Average acceleration = total change in velocity/total time taken
The average acceleration can be positive or negative depending upon the sign of change of velocity.It is 0 if the change in velocity of the object in the given interval of time is 0.
Graphical Representation of Motion
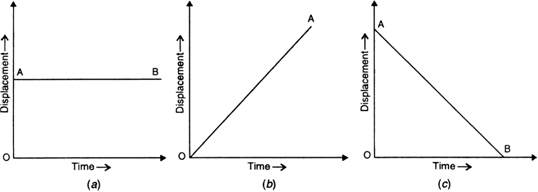
Displacement-Time graph:
I.When an object is at rest
Then the graph is a straight line parallel to time axis.
II.When an object is moving with 0 acceleration
Then the graph is a straight line with positive slope and the object is initially at some distance from the origin.
III.When an object is moving with uniform positive acceleration
Then the graph is curve with positive slope and the object is at some distance from the origin.
IV. When an object is moving with negative acceleration
Then the graph is a curve with negative slope and the object is initially at some distance from the origin.

Velocity-Time graph
I.When an object is moving with constant velocity(0 acceleration)
Then the graph is a straight line parallel to time axis.same as displacement-time graph when object is at rest.
II.When an object is moving with positive constant acceleration having some initial velocity
Then the graph is straight line.
III.When an object is moving with constant positive acceleration having zero initial velocity
Then the graph is a straight line passing through the origin.fig(b)
IV.When an object is moving with increasing acceleration having zero initial velocity
Then the graph is a curve.fig(c)

Equations of motion
The three equations on a straight line are
1.v=u+at 2.s=ut+1/2at^2 3.v^2-u^2=2as
Where v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity,a is uniform acceleration of the body,s is the distance travelled in this time t is time.
Free Falling objects
The objects falling towards the earth under the gravitational force alone,are called freely falling objects and such fall is called free fall.
Whenever an object falls towards earth,an acceleration is involved,this acceleration is due to the gravitational pull and is called acceleration due to gravity
Acceleration due to gravity near the earth surface is 9.8m/s^2.
Cases of free fall
>If an object falls vertically downward then acceleration due to gravity is taken as positive.its initial velocity is 0
>If an object is thrown vertically upward then acceleration due to gravity is taken as negative.its final velocity is 0.
Circular motion
The motion in which a particle moves along a circular path,is called circular motion.terms related to circular motion
I.Time period:In circular motion,the time period is defined as the time taken by the particle to complete one revolution on circular path.its unit is second.
II.Frequency:The frequency is defined as the number of revolutions completed by the object on its circular path in a unit time.its unit is s^-1 or hertz.
III.Angular displacement:The angular displacement of the object in a given time,moving around a circular path is defined as the angle swept by the radius of the circular path in the given time.its unit is radian.
Angular displacement =Arc/Radius
IV.Angular velocity:The time rate of change of its angular displacement.its unit is radian/sec.
Angular velocity =Angular displacement/Time.
Angular Acceleration: The time rate of change of its angular velocity.its unit is radian/sec^2.
The three equations on a straight line are
1.v=u+at 2.s=ut+1/2at^2 3.v^2-u^2=2as
Where v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity,a is uniform acceleration of the body,s is the distance travelled in this time t is time.
Free Falling objects
The objects falling towards the earth under the gravitational force alone,are called freely falling objects and such fall is called free fall.
Whenever an object falls towards earth,an acceleration is involved,this acceleration is due to the gravitational pull and is called acceleration due to gravity
Acceleration due to gravity near the earth surface is 9.8m/s^2.
Cases of free fall
>If an object falls vertically downward then acceleration due to gravity is taken as positive.its initial velocity is 0
>If an object is thrown vertically upward then acceleration due to gravity is taken as negative.its final velocity is 0.
Circular motion
The motion in which a particle moves along a circular path,is called circular motion.terms related to circular motion
I.Time period:In circular motion,the time period is defined as the time taken by the particle to complete one revolution on circular path.its unit is second.
II.Frequency:The frequency is defined as the number of revolutions completed by the object on its circular path in a unit time.its unit is s^-1 or hertz.
III.Angular displacement:The angular displacement of the object in a given time,moving around a circular path is defined as the angle swept by the radius of the circular path in the given time.its unit is radian.
Angular displacement =Arc/Radius
IV.Angular velocity:The time rate of change of its angular displacement.its unit is radian/sec.
Angular velocity =Angular displacement/Time.
Angular Acceleration: The time rate of change of its angular velocity.its unit is radian/sec^2.
Please SUBSCRIBE





0 Comments